Why Performance Reporting is NOT Performance Management!
03/04/2017

“Mirror, mirror on the wall whose presentation is the fairest of them all?”
“GDP last quarter is higher than the previous quarter, and the same quarter last year”, says Kamal Ahmed of the BBC News. So far his reporting is correct. “Therefore it’s improving!”, and that’s where his performance management is wrong! The accurate thing that he can say looking at GDP data like this is “Therefore it’s different!”
There’s a massive chasm between reporting what has happened in the past and claiming it tells us about performance management – i.e. about what is likely to happen going forward. Let’s look at 3 aspects of this little conundrum:
- How can we better understand what has happened in the past (in order to take more appropriate action going forward)
- What can we say about what is likely to happen going forward (with/without any intervention)
- What are the fundamental differences between Performance Reporting and Performance Management
Let’s go back to Kamel Ahmed, and to keep things less controversial for this piece, we’ll look at GDP for the UK (figures from the World Bank – and let’s not get into which sources of figures best suit what position we want to take, or who can present the fairest of them all) on an annual basis up to and including 2011. The first thing you’ll notice is (refer back to previous posts on this matter) we are not showing % increases. The misleading reporting we hear and see around the %GDP increase this period (month, quarter, year) is x% better than last period – as if there is some God-given right that %GDP should always be increasing (we are living in a finite world!). If this was indeed the case, then we would be see raw GDP increase exponentially! That looks something like this:
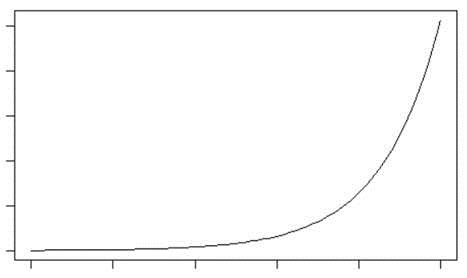
This would mean infinite raw GDP sometime soon. “Unrealistic!” you might say!
So what does raw GDP actually look like:
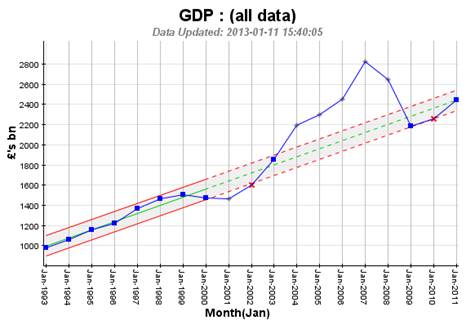
Interesting! I only have the figures back to 1993, but you have to start somewhere! We are showing the annual figures within trended (Extended-SPC, see previous posts) guidelines – and it is the pattern and trend we should look at as much as the actual individual annual results. We can see up until the credit boom in the early 2000s GDP was trending upwards at about £100bn per year (not unhealthy!). Then GDP dipped around the bursting of the “dotcom bubble”, around 2000 – 2002, and then went nuts with the credit fuelled economy. Then there was a correction (some say disaster, but, as I say, we are living in a finite world!) around 2007/2008. And guess what, the following 3 years where everyone thought we were in “plateau-land” (percentages!) GDP returned to the previous upward trend established in the earlier part of the chart.
Is this a better way of looking at Performance in order to understand it? I’ll leave that with the reader …. and next time we’ll have a look at house prices in the same way, and see if we can see a pattern. After that? We’ll attempt to answer the final two questions posed above…
David Anker
Categories & Tags:
Leave a comment on this post:
You might also like…
Company codes – CUSIP, SEDOL, ISIN…. What do they mean and how can you use them in our Library resources?
As you use our many finance resources, you will probably notice unique company identifiers which may be codes or symbols. It is worth spending some time getting to know what these are and which resources ...
Supporting careers in defence through specialist education
As a materials engineer by background, I have always been drawn to fields where technical expertise directly shapes real‑world outcomes. Few sectors exemplify this better than defence. Engineering careers in defence sit at the ...
What being a woman in STEM means to me
STEM is both a way of thinking and a practical toolkit. It sharpens reasoning and equips us to turn ideas into solutions with measurable impact. For me, STEM has never been only about acquiring ...
A woman’s experience in environmental science within defence
When I stepped into the gates of the Defence Academy it was the 30th September 2019. I did not know at the time that this would be the beginning of a long journey as ...
Working on your group project? We can help!
When undertaking a group project, typically you'll need to investigate a topic, decide on a methodology for your investigation, gather and collate information and data, share your findings with each other, and then formally report ...
From passion to purpose: My journey at the Pinnacle of Aviation
By: Sultana Yassin Abdi MSc Air Transport Management, Current Student Born and raised in the vibrant landscape of the UAE, with roots stretching back to Somalia, my life has always been ...