A muddy river in a bigger picture
11/07/2019
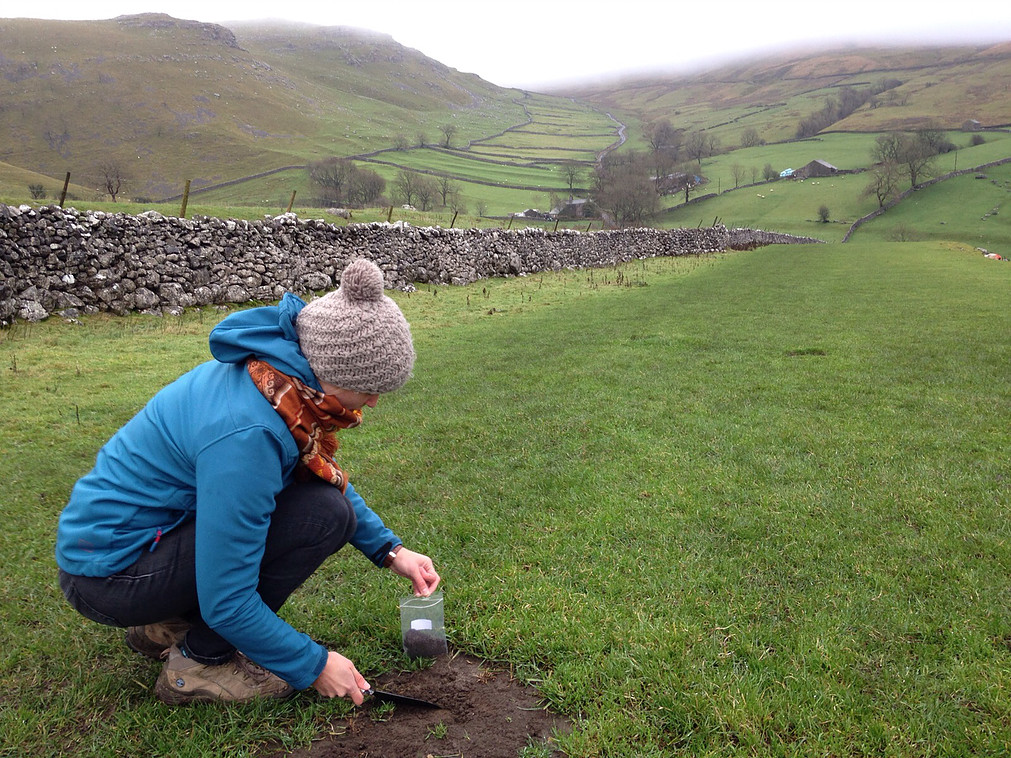

Two years ago I completed my PhD at Cranfield University. Now, after a postdoc at University of Leeds, I am back at Cranfield working on a NERC-funded project on social-economic-environmental trade-offs in managing the land-river interface. The start of my new job at Cranfield coincided with the publication of the last paper of my PhD, called “Temporal variation in suspended sediment transport: linking sediment sources and hydro-meteorological drivers”. So, before getting into the exciting details of the new project, let’s talk about sediment!
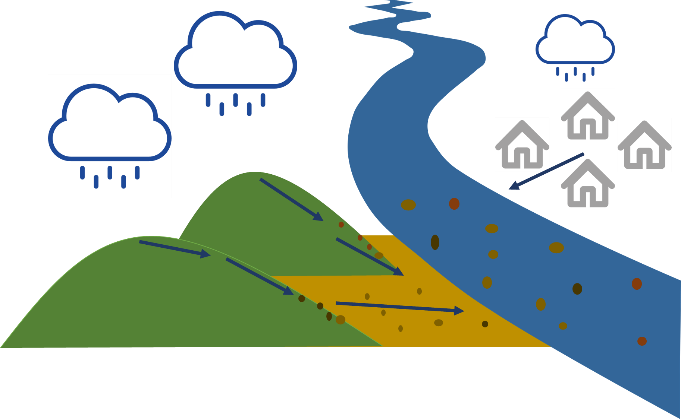
What do we mean by suspended sediment? Well, basically, when it rains and water falls onto the earth’s surface, it can cause very fine particles (from different surfaces, such as soils and streets) to be transported together with the flowing water towards the river. Once the particles are in the river, we call it sediment. Sediment is an important aspect of rivers, as these particles carry nutrients from the land and they form the building blocks of aquatic habitats. However, too much sediment can also cause problems to these habitats, and sediment particles are also known to carry pollutants. Therefore, scientists and river managers are very much interested in understanding sediment transport in rivers.
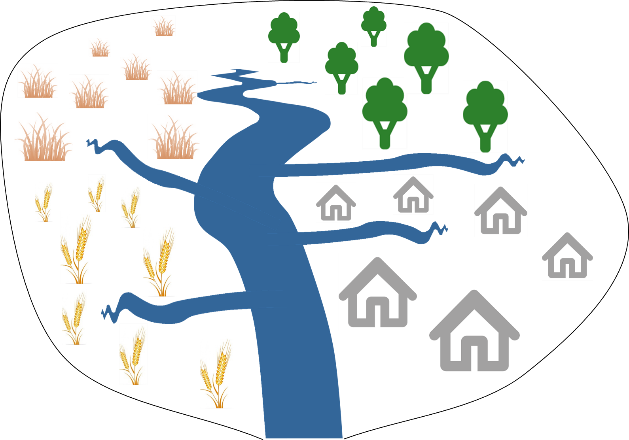
Let’s now zoom out a bit and look at an entire river catchment that consists of four types of land use (grassland, forest, agriculture, urban). Suppose it starts raining and particles are being transported from land towards the river from all across the catchment (situation 1). As a result of this, we get a mixture of sediment coming from the surface of the four types of land use. Alternatively, when it is only raining in the upper left part of the catchment, we get mainly particles from the grassland area (situation 2), while only rain in the right part of the catchment will mainly cause particles from forest and urban area to be transported to the river (situation 3).
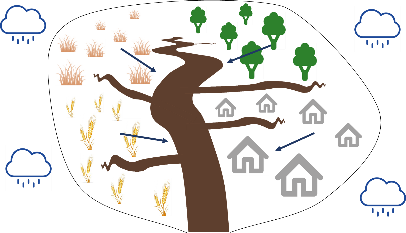

Situation 2: rainfall in upper left part of the catchment
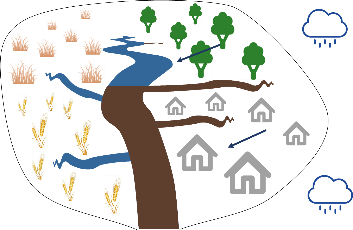
Situation 3: rainfall in right part of the catchment
In each of these three situations, the amount and source of the sediment will be different. However, if we take a sediment sample at the outlet of the river catchment in each of these situations, we can calculate how much sediment is in our sample, but we cannot actually see where the sediment comes from. From the mixed sediment sample, we simply cannot see what the main sources of the sediment are.
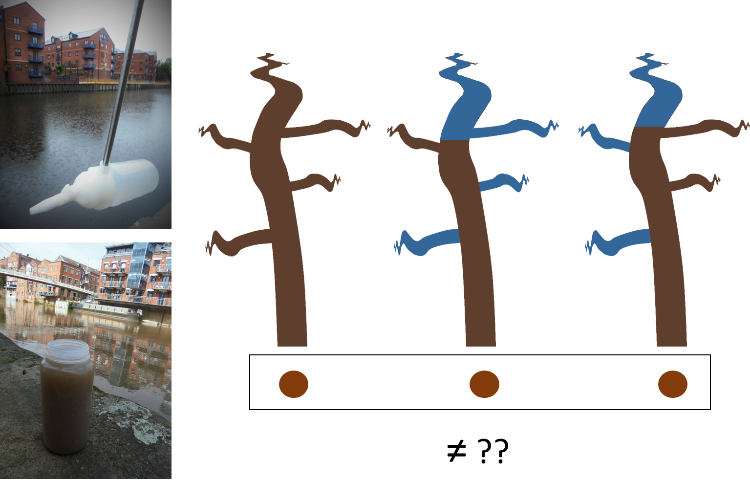
Why would we want to know the source of the sediment? Understanding how much sediment there is in the river, where it comes from, and how it varies over time as a result of variations in rainfall, provides very important information that can help us better predict and monitor fine sediment in rivers and develop targeted management strategies. But because sediment studies in rivers are based on the mixed sediment samples, we miss important information about the bigger picture (catchment).
That is why our recently published paper applied a technique called “sediment fingerprinting”, which basically aims at identifying the sources of sediment in a mixed sample. The technique characterises sediment from the different sources (land use types) (which we did using Infrared Spectroscopy), and then include these characteristics into a statistical model to “un-mix” our samples into the contributions of the sources.
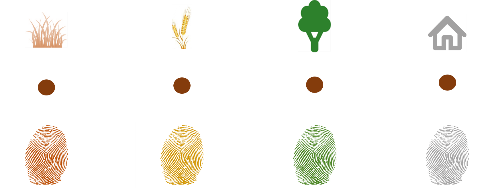
Identifying the sediment fingerprint of each sediment source
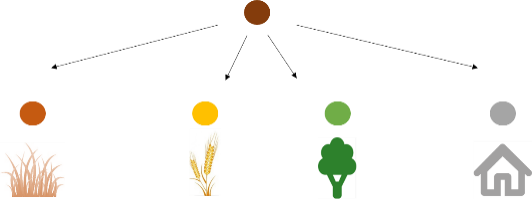
Un-mixing sediment sample in contributions of sediment sources with statistical model
We applied this technique to the River Aire in Leeds (UK) to identify the most important sediment sources of fine sediment in the River Aire, and most importantly, investigate how these sources vary over time as a result of variations in rainfall and river flow. By linking information obtained through sediment fingerprinting with detailed rainfall and river discharge data, we were able to construct a bigger (sediment) picture for the River Aire catchment.
Categories & Tags:
Leave a comment on this post:
You might also like…
My journey to Cranfield as an FIA Motorsport Engineering Scholar
"You don’t need to fit a stereotype to succeed in engineering or motorsport. You need curiosity. Resilience. And the confidence to take up space." In this blog, Sanya Jain, current MSc student and FIA ...
‘Getting started with Bloomberg’ training – discover the power of Bloomberg terminals
Perhaps you've heard people talking about Bloomberg or heard it mentioned in the news and are wondering what all the fuss is about? Why not come along and find out at our Getting started with ...
Commonwealth Scholarships play a critical role in developing sustainability and leadership in Africa
Q&A with Evah Mosetlhane, Sustainability MSc, Commonwealth Distance Learning Scholar What inspired you to pursue the Sustainability MSc at Cranfield? I was inspired to pursue the Sustainability MSc at Cranfield because of the university’s ...
How do I reference a thesis… in the NLM style?
You may be including theses within your research. When you do so you need to treat them in the same way as content taken from any other source, by providing both a citation and a ...
Introducing… Bloomberg Trade Flows
Are you interested in world trade flows? Would it be useful to know which nations are your country's major trading partners? If so, the Bloomberg terminal has a rather nifty function where you can view ...
Cranfield alumni voyage to the International Space Station
Seeing our alumni reach the International Space Station (ISS) has a ripple effect that extends far beyond the space sector. For school students questioning whether science is “for them”, for undergraduates weighing their next ...