‘Drones for Good’: Remotely Piloted Aircraft Systems (RPAS) helping investigators gather evidence and prevent future accidents
01/04/2016
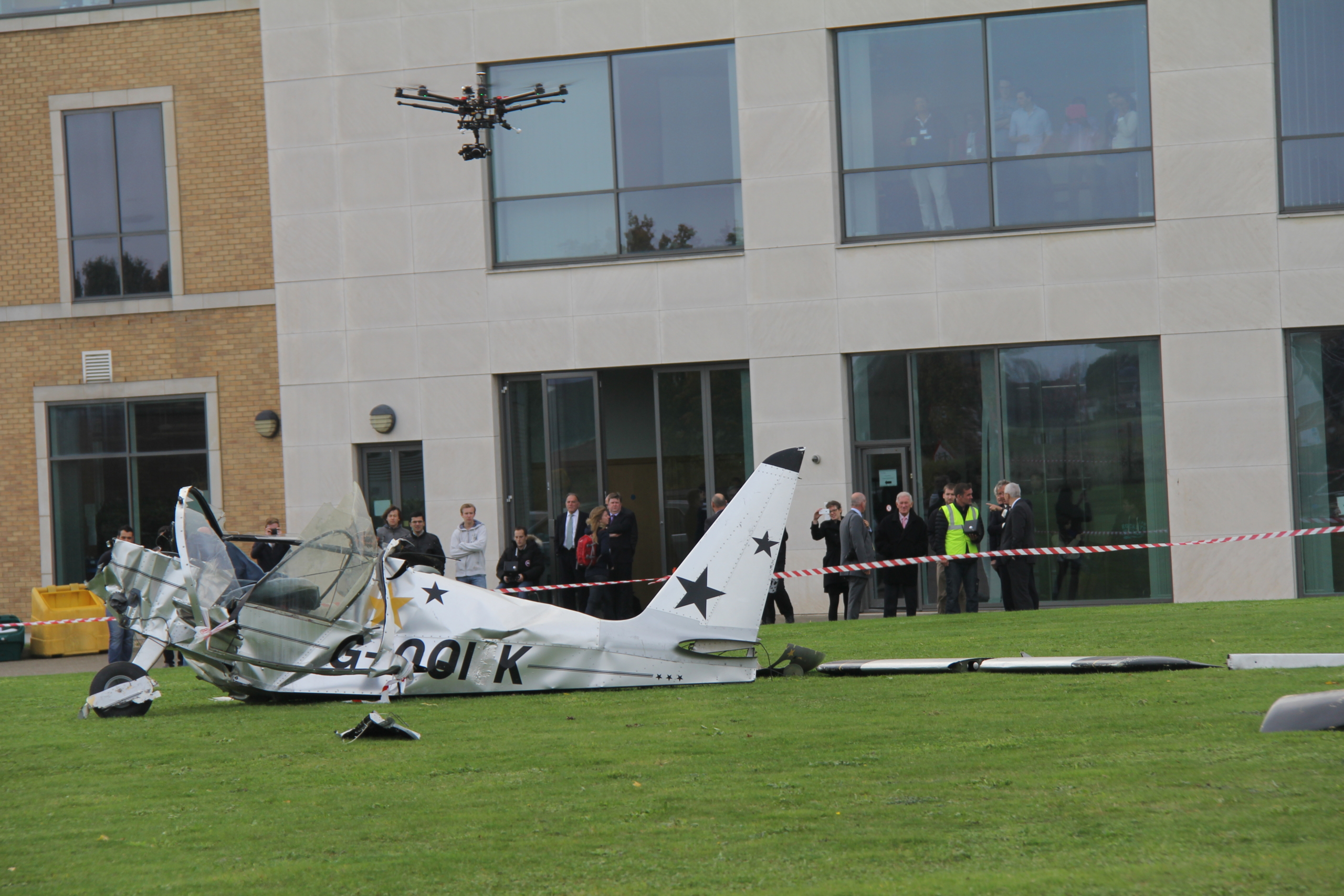

Photo: DJI S1000 “Octocopter” Drone scans a demo accident site outside Martell House, Cranfield University
Accident sites are often dangerous or difficult places to work. There are always hazards that will require the accident investigator to expose themselves to risk. These take many forms – environmental, physical, material, biological, psychological – which will need to be addressed, as the investigator needs to collect as much evidence (particularly perishable evidence which might be washed away, blown away or destroyed) as quickly as possible.
During this initial risk assessment the RPAS cameras (video/stills/thermal/Infrared) are capturing this evidence. This imagery will then be used in real time to assist with communicating the situation to other agencies. This helps confirm the extent of the accident site or even control access, if required.
RPAS allows the investigator to conduct a dynamic risk assessment from a distance whilst also capturing the evidence required with video and stills. Previously helicopters or fixed wing aircraft might have been chartered to provide this service. This is expensive and not always practical.
Based upon the utility outlined above RPAS technology is currently being used by state level investigation agencies including UK Air Accidents Investigation Branch (AAIB) and the UK Rail Accident Investigation Branch (RAIB).
This technology is improving week by week, and some of the best results are being achieved with some of the smallest and most readily available systems.
A key point to the success of their deployment is that they are operated legally and safely by professionals who understand the airspace in which they might operate, but also the hazards present at the accident.
Cranfield University is leading the way in this field. At the Safety and Accident Investigation Centre we continue to test theories and push investigative/research boundaries on the accident site. Flying a range of drones, with a wide array of sensors, we aim to enhance current accident investigation techniques. But more than this we aim to revolutionise how evidence is gathered, analysed and then promulgated to the public and wider safety community.
An example of this is our work with 3D models. We are pioneering new 3D modelling techniques in order to provide accurate, measurable 3D models of accident sites (using the video and stills captured for evidence collection, then applying photogrammetry techniques to convert these images to 3 D models). These can then be used for investigative analysis, and as graphic representation in final accident reports.
This is a hugely exciting area of research, which utilises new and innovative drone technology and gives us an advantage when investigating serious accidents and incidents. Constantly looking to the future, our aim is to continue to be the centre of excellence with regard to this novel and innovative approach.
Categories & Tags:
Leave a comment on this post:
You might also like…
Keren Tuv: My Cranfield experience studying Renewable Energy
Hello, my name is Keren, I am from London, UK, and I am studying Renewable Energy MSc. My journey to discovering Cranfield University began when I first decided to return to academia to pursue ...
3D Metal Manufacturing in space: A look into the future
David Rico Sierra, Research Fellow in Additive Manufacturing, was recently involved in an exciting project to manufacture parts using 3D printers in space. Here he reflects on his time working with Airbus in Toulouse… ...
A Legacy of Courage: From India to Britain, Three Generations Find Their Home
My story begins with my grandfather, who plucked up the courage to travel aboard at the age of 22 and start a new life in the UK. I don’t think he would have thought that ...
Cranfield to JLR: mastering mechatronics for a dream career
My name is Jerin Tom, and in 2023 I graduated from Cranfield with an MSc in Automotive Mechatronics. Originally from India, I've always been fascinated by the world of automobiles. Why Cranfield and the ...
Bringing the vision of advanced air mobility closer to reality
Experts at Cranfield University led by Professor Antonios Tsourdos, Head of the Autonomous and Cyber-Physical Systems Centre, are part of the Air Mobility Ecosystem Consortium (AMEC), which aims to demonstrate the commercial and operational ...
Using grey literature in your research: A short guide
As you research and write your thesis, you might come across, or be looking for, ‘grey literature’. This is quite simply material that is either unpublished, or published but not in a commercial form. Types ...





I would imagine that quadcopters are the drones of choice for use in these situations. What about fixed wing systems?