Systematic Literature Review – Identifying your search terms and constructing your search strings
28/03/2024

Our previous posts on the systematic review have looked at getting started and selecting your sources. In this post we will look at the next fundamental stage:
- Identifying your search terms and constructing your search strings
Identifying your search terms
Having decided which sources you need to search, the next step in the systematic literature review process is to identify your search terms or keywords:
- These may be individual words such as customer, or phrases like “customer research management”. Note: if phrases are not inserted inside double quotation marks, each word will be searched for individually rather than as a phrase, e.g., customer AND service AND management instead of “customer service management”.
- Your search terms should consist of not just the words which are included in your research question, but also synonyms (e.g. customer OR consumer), spelling variants, and any relevant concepts.
- Spelling variants such as organization and organisation can be dealt with by using the wildcard symbol (‘?’) in place of a single letter. For example, a search for ‘organi?ation’ will look for both spellings of the word. Note: not all sources accept the wildcard symbol. Check the search tips of your resource for guidance.
- Use the truncation symbol (‘*’) at the end of a whole or partial word to search for variant word endings. For example, strateg* will find strategy, strategies, strategic etc. Note: not all sources accept the truncation symbol. Check the search tips of your resource for guidance.
When choosing your keywords, remember that the aim is to identify all relevant literature without making the search so broad that you retrieve lots of irrelevant material. For example, the synonyms for customer in the example below have been combined into a search string using the word OR:
(consumer OR customer OR client OR user)
Note that words such as individual or subject have not been included as these words are homographs and would produce a lot of irrelevant material. Homographs are words that are spelled the same but have more than one meaning. You should also only use ‘sensible synonyms’. For example, in gender studies you would not search using terms such as ‘gentleman’ or ‘lady’. These terms are unlikely to be used by the scholars in your field.
Constructing your search strings
Once you have chosen your keywords and phrases, they can be combined into search strings. Some examples of search strings are given below:
String 1 (“supply chain*” OR “supply network*” OR “demand chain*” OR “demand network*” OR “value chain*” OR “value network*”)
String 2 (“lead time compression” OR “lead time reduction” OR “cycle time compression” OR “cycle time reduction” OR “dwell time compression” OR “dwell time reduction”)
String 3 (agil* OR “quick response” OR speed*)
Note that each search string only contains synonyms or related terms.
Now that you have created your search strings, you are ready to construct your search strategies.
Other blog posts you may find useful
- Systematic Literature Review – Where do I begin?
- Systematic Literature Review – Selecting your Sources
Contact us
Because of the complexity of this process, we recommend that before embarking on a systematic literature review you speak with your Librarian who will be happy to provide guidance.
Categories & Tags:
Leave a comment on this post:
You might also like…
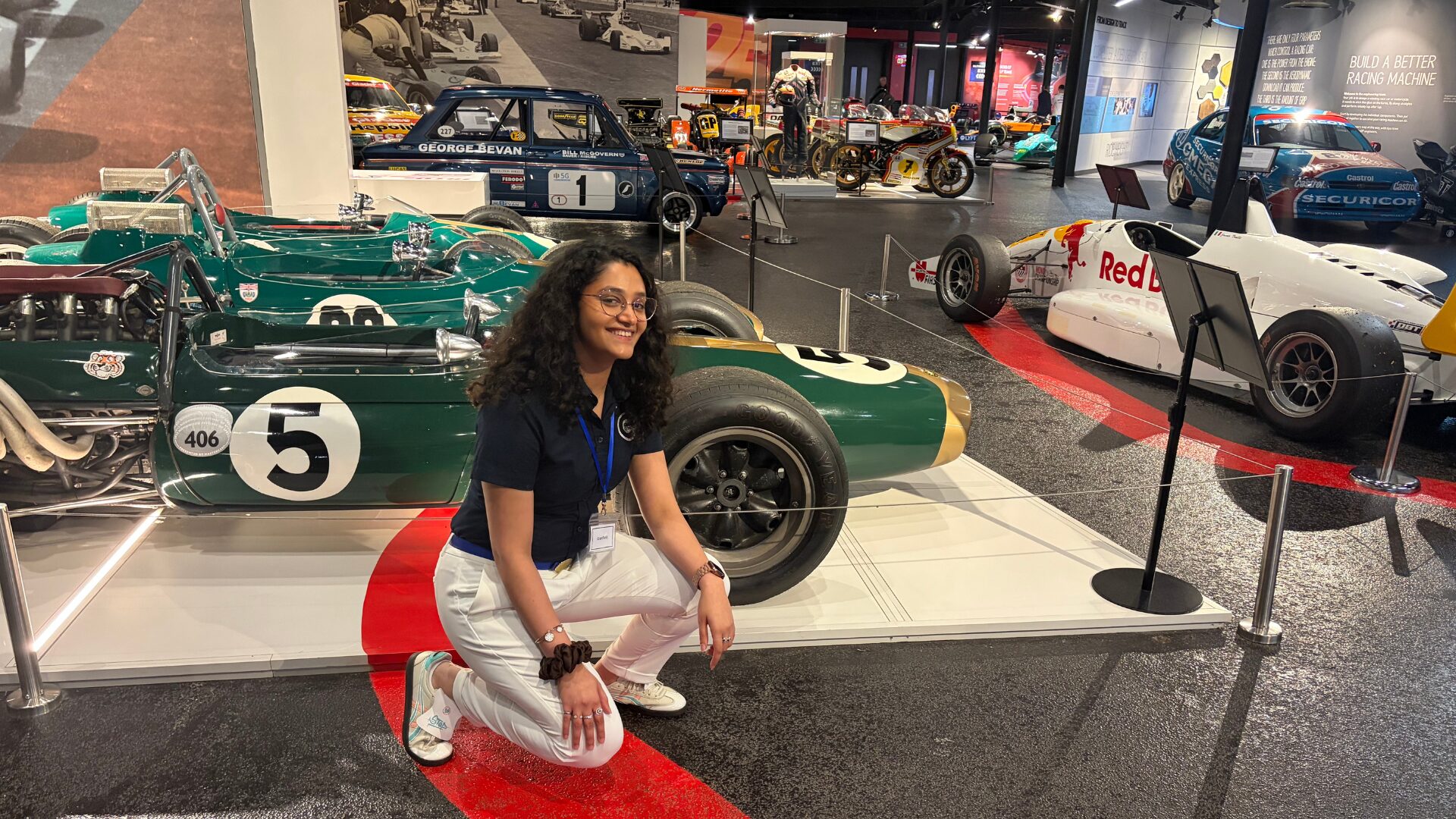
My journey to Cranfield as an FIA Motorsport Engineering Scholar
"You don’t need to fit a stereotype to succeed in engineering or motorsport. You need curiosity. Resilience. And the confidence to take up space." In this blog, Sanya Jain, current MSc student and FIA ...
‘Getting started with Bloomberg’ training – discover the power of Bloomberg terminals
Perhaps you've heard people talking about Bloomberg or heard it mentioned in the news and are wondering what all the fuss is about? Why not come along and find out at our Getting started with ...
Commonwealth Scholarships play a critical role in developing sustainability and leadership in Africa
Q&A with Evah Mosetlhane, Sustainability MSc, Commonwealth Distance Learning Scholar What inspired you to pursue the Sustainability MSc at Cranfield? I was inspired to pursue the Sustainability MSc at Cranfield because of the university’s ...
How do I reference a thesis… in the NLM style?
You may be including theses within your research. When you do so you need to treat them in the same way as content taken from any other source, by providing both a citation and a ...
Introducing… Bloomberg Trade Flows
Are you interested in world trade flows? Would it be useful to know which nations are your country's major trading partners? If so, the Bloomberg terminal has a rather nifty function where you can view ...
Cranfield alumni voyage to the International Space Station
Seeing our alumni reach the International Space Station (ISS) has a ripple effect that extends far beyond the space sector. For school students questioning whether science is “for them”, for undergraduates weighing their next ...






Comments are closed.