Performance Reporting Measures vs Performance Management Measures – Part 2
05/12/2019
Another Problem with % Measures
You may have read my blog from last week comparing Performance Reporting Measures vs Performance Management Measures.
Performance reporting is littered with measures that may appear to carry meaning for some people, but in our observations, have been misleading and impenetrable to many. And certainly don’t help understanding nor how to improve!
Here are some examples of reporting measures that we introduced previously:
- % items completed: % implies a ratio – with a numerator and denominator. E.g. % Repairs Completed defined by (Number of Repairs Completed / Total Number of Repair Calls) * 100
- % completed within some timeframe: E.g. From a previous blog’s A&E Figures, we saw % A&E attendants seen in 4 hours or under.
- Complicated Measure Combinations: E.g. % Forecast Accuracy in Supply-chain
- Applying sophisticated statistical treatment to raw performance measures that only stats specialists can read: E.g. Exponentially weighted moving averages
- Statistical representation of a population of people or things: E.g. Electric Car Use by Country
There’s one more critical problem with % measures I didn’t mention last time. And this one is particularly mind-bending, even to some of those who have studied Maths!
You start to stumble across the problem when you start drilling down into sub-sets of the data to “better understand what is going on”. So, for example, regarding A&E data, you may want to drill down by hospital and by age-group. You do this at your peril!
But, to keep this light, we’ll select an alternative example from Wikipedia that you can all go take a look at – batting percentages over two years for two baseball players. We could have picked a cricketing example, but who knows what’s happening in the Test in New Zealand right now – well I said I wanted to keep this light!
So here are the baseball figures – the figures are (number of hits) / (number of “at bats”):
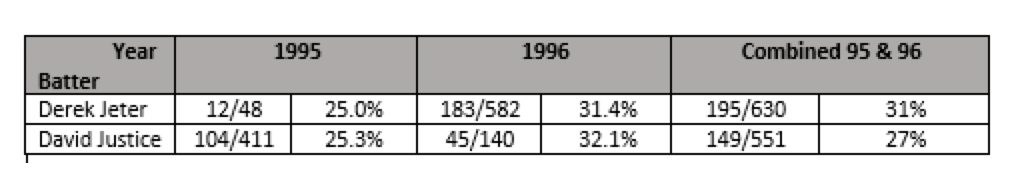
So looking at the individual year’s batting % in each of 1995 and 1996, you’d want to bet on David Justice. BUT! When you look at their combined % for the 2 years, you’d want to go with Derek Jeter. Confused?
I won’t explain this paradox here, since Wiki does a very good job of it – but it is well-known (to some mathematicians and stats guys) as Simpson’s Paradox. It happens because both the numerator and denominator can vary independently.

The ONLY way to resolve this is to have a clear PURPOSE for the business process (Wiki refers to STORY), which will guide the reader on whether to use the aggregated % or the component %s, OR to use an alternative measure altogether.
And I’m pretty sure Dilbert would encourage you to look at the underlying raw data – i.e. number of “at bats” and the “hits” separately (instead of, or, worst case, as well as %’s) if you really want to understand what’s happening!
Categories & Tags:
Leave a comment on this post:
You might also like…
Keren Tuv: My Cranfield experience studying Renewable Energy
Hello, my name is Keren, I am from London, UK, and I am studying Renewable Energy MSc. My journey to discovering Cranfield University began when I first decided to return to academia to pursue ...
3D Metal Manufacturing in space: A look into the future
David Rico Sierra, Research Fellow in Additive Manufacturing, was recently involved in an exciting project to manufacture parts using 3D printers in space. Here he reflects on his time working with Airbus in Toulouse… ...
A Legacy of Courage: From India to Britain, Three Generations Find Their Home
My story begins with my grandfather, who plucked up the courage to travel aboard at the age of 22 and start a new life in the UK. I don’t think he would have thought that ...
Cranfield to JLR: mastering mechatronics for a dream career
My name is Jerin Tom, and in 2023 I graduated from Cranfield with an MSc in Automotive Mechatronics. Originally from India, I've always been fascinated by the world of automobiles. Why Cranfield and the ...
Bringing the vision of advanced air mobility closer to reality
Experts at Cranfield University led by Professor Antonios Tsourdos, Head of the Autonomous and Cyber-Physical Systems Centre, are part of the Air Mobility Ecosystem Consortium (AMEC), which aims to demonstrate the commercial and operational ...
Using grey literature in your research: A short guide
As you research and write your thesis, you might come across, or be looking for, ‘grey literature’. This is quite simply material that is either unpublished, or published but not in a commercial form. Types ...