3D Metal Manufacturing in space: A look into the future
26/07/2024
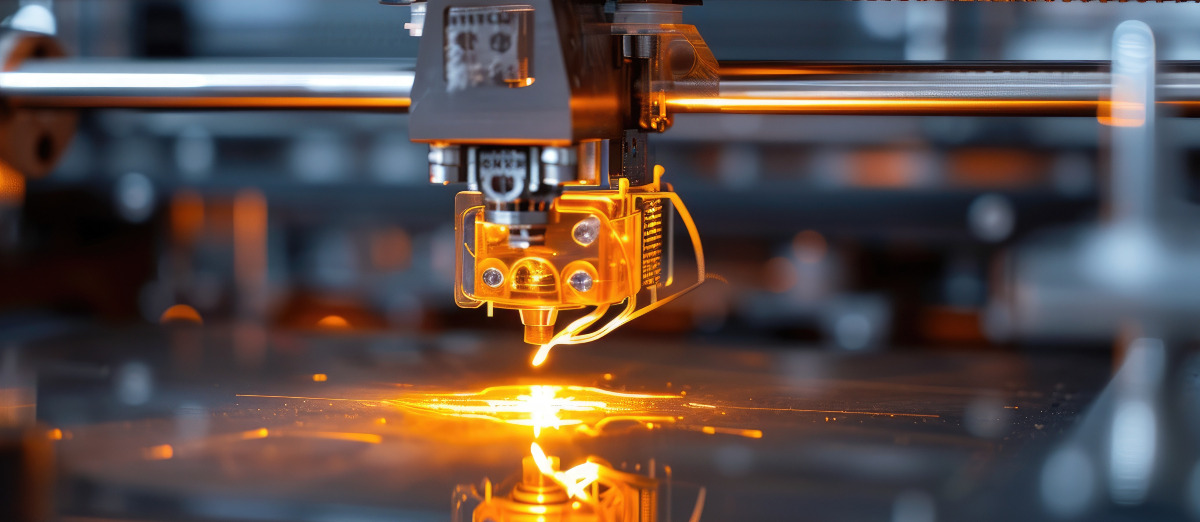
David Rico Sierra, Research Fellow in Additive Manufacturing, was recently involved in an exciting project to manufacture parts using 3D printers in space. Here he reflects on his time working with Airbus in Toulouse…
When you are offered the chance to work on a project at Airbus, one of the biggest companies in the aerospace industry, you don’t say “I’ll think about it.” So when I was fortunate enough to be offered work on a short-term, interdisciplinary project at Airbus HQ in Toulouse, France, I jumped at the chance! I was there to contribute my expertise in additive manufacturing to a team made up of people from all over Europe. It was rewarding and challenging in equal measure.
Creating an automated ‘space factory’
The goal of the project was to show that it was possible to create a fully automated ‘space factory’ for spare parts as part of the Star Tiger Initiative from the European Space Agency. We wanted to find out how to integrate two different printers – a Carbon Fibre Reinforced Plastics (CFRP) 3D printer and a metal 3D printer – in conjunction with robotic arms that assemble the parts after they’ve been printed. The project was a feasibility study to show that it was possible to produce, verify and assemble CFRP and metallic parts produced in the two printers, creating a modular part of a satellite antenna.
My role was to help find a solution for one of the main challenges in using a metal printer – finding the correct set of parameters and techniques to remotely remove a small, printed metallic part from the printer, and the separation of that part without additional tooling and little-to-no human interaction.
That meant first fully understanding the capabilities of the newly produced 3D metal printer, which was a replica of the one sent to the International Space Station (ISS) in January 2024. This was key, because we needed to be able to reliably produce metallic parts from it, modifying methods and parameters to meet our objectives.
The second challenge was to produce a small, metallic part which would be easily detachable from the base layer inside the printer in an automated process. Although it sounds a simple thing, this was a seriously complex task and presented a few headaches and frustrations!
In most 3D printers the part being built is secured to the substrate to provide a stable and reliable base for adding the next layer of material. This is why the metallic parts produced in 3D printers require additional tooling to separate the part from the substrate – in this case some kind of metal cutting equipment. However, additional equipment and resources are limited on the ISS, and this would also increase the complexity of the system. Given that one of the goals was to make the process fully automated, this was a real challenge for the team.
Collaboration, diversity and innovation made it unforgettable
The team was made up of people with vastly different backgrounds and experiences. Early on that meant a learning curve in terms of finding ways to work together, but ultimately that diversity of experience was an invaluable asset, with varied backgrounds and approaches uniting to address the complexity of the goals.
One of the most important takeaways from this project was to understand what it’s like to work with the support of a huge company like Airbus. They’re one of the leading players in the aerospace sector and have a broad range of knowledge about working with space-focussed projects.
On a personal level, my part of the project was filled with challenges and sometimes even frustrations, but the continuous support from the whole team at Airbus, and my supervisor at Cranfield, helped me succeed. At the end of the project we gave a demonstration of the process in front of ESA representatives. It was well received and a proud moment not only for me but for the whole team, who worked tirelessly to make sure that the project was a success.
I’m very grateful to have had the opportunity to work with Airbus. I was rewarded with wonderful experiences but also complex challenges and the enthusiasm for collaboration, desire for excellence and innovation made this project unforgettable.
Categories & Tags:
Leave a comment on this post:
You might also like…
My journey to Cranfield as an FIA Motorsport Engineering Scholar
"You don’t need to fit a stereotype to succeed in engineering or motorsport. You need curiosity. Resilience. And the confidence to take up space." In this blog, Sanya Jain, current MSc student and FIA ...
‘Getting started with Bloomberg’ training – discover the power of Bloomberg terminals
Perhaps you've heard people talking about Bloomberg or heard it mentioned in the news and are wondering what all the fuss is about? Why not come along and find out at our Getting started with ...
Commonwealth Scholarships play a critical role in developing sustainability and leadership in Africa
Q&A with Evah Mosetlhane, Sustainability MSc, Commonwealth Distance Learning Scholar What inspired you to pursue the Sustainability MSc at Cranfield? I was inspired to pursue the Sustainability MSc at Cranfield because of the university’s ...
How do I reference a thesis… in the NLM style?
You may be including theses within your research. When you do so you need to treat them in the same way as content taken from any other source, by providing both a citation and a ...
Introducing… Bloomberg Trade Flows
Are you interested in world trade flows? Would it be useful to know which nations are your country's major trading partners? If so, the Bloomberg terminal has a rather nifty function where you can view ...
Cranfield alumni voyage to the International Space Station
Seeing our alumni reach the International Space Station (ISS) has a ripple effect that extends far beyond the space sector. For school students questioning whether science is “for them”, for undergraduates weighing their next ...







Comments are closed.