Renewable heating and cooling to slash carbon emissions
07/07/2022

Domestic/commercial applications: Energy consumption in the building sector accounts for 40% of the total energy consumption worldwide. The UK has set the goal of achieving NetZero by 2050. In 2012, the UK had a total greenhouse gas emission level of 613 MtCO2e. Residential buildings and non-residential buildings have shares of 12% and 3%, respectively. There is an urgent demand to increase the share of renewable energy sources and reduce carbon emissions, which is essential to the energy efficiency policy in the UK. “Greener Buildings” is part of the UK Prime Minister’s ten-point plan (point 7) to achieve a green industrial revolution in the UK, with an aim of attracting around £11bn private investment in 2020, supporting approximately 50,000 jobs in 2030 and savings of 71MtCO2e between 2023 and 2032. At present, building cooling and heating is mostly achieved by electricity and fuel such as natural gas. Solar energy combined with thermal energy storage has the potential to meet the combined heating and cooling demand of buildings by greener means.
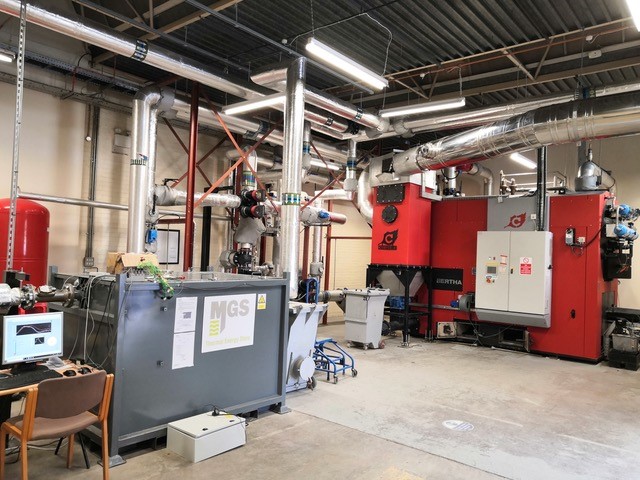
More recently Cranfield University and EGB Engineering have been successful in securing funding from Innovate UK for industrial research into low-carbon renewable heating and cooling systems to decarbonise public and commercial buildings. The development of thermal energy storage via phase change material, and solar evacuated tube collectors to capture renewable heat and turn them into cooling through an absorption chiller to increase the renewable share in the building cooling applications. This project has supported the construction of several components and testing its performance in a realistic environment: solar evacuated tube collectors and the heat storage system (figure 1).



Figure 1: 1.2 kW evacuated tube collector, 120kWth PCM storage connected to Cranfield heat networks and 1kW lab scale PCM capability.
Waste heat recovery: In any conventional power generation cycle (eg; steam Rankine cycle) two-thirds of the energy is dumped into the atmosphere, yet this low-quality heat can be captured and utilised to operate the thermal driven absorption chillers and provide the cooling loads to nearby buildings. This novel approach formed part of an EU FP7 funded project (MATS) to design an absorption chiller from a 1MWe turbine waste heat and understand its thermodynamic performance. The follow-on project supported by Newton-British council with EJUST to build an integrated community level system for Egypt, 10kW electricity, 1m3/day of water 10 kW cooling load including cold storage.
Overall, these activities helped to assess the market potential of this technology, and to increase the proportion of renewable energy in the heating and cooling sectors and reduce the reliance on fossil fuels. The group is exploring options for the integration of these designs into Cranfield’s own heat/cooling networks.
Categories & Tags:
Leave a comment on this post:
You might also like…
Introducing… Bloomberg Trade Flows
Are you interested in world trade flows? Would it be useful to know which nations are your country's major trading partners? If so, the Bloomberg terminal has a rather nifty function where you can view ...
Cranfield alumni voyage to the International Space Station
Seeing our alumni reach the International Space Station (ISS) has a ripple effect that extends far beyond the space sector. For school students questioning whether science is “for them”, for undergraduates weighing their next ...
From classroom to cockpit: What’s next after Cranfield
The Air Transport Management MSc isn’t just about learning theory — it’s about preparing for a career in the aviation industry. Adit shares his dream job, insights from classmates, and advice for prospective students. ...
Setting up a shared group folder in a reference manager
Many of our students are now busy working on their group projects. One easy way to share references amongst a group is to set up group folders in a reference manager like Mendeley or Zotero. ...
Company codes – CUSIP, SEDOL, ISIN…. What do they mean and how can you use them in our Library resources?
As you use our many finance resources, you will probably notice unique company identifiers which may be codes or symbols. It is worth spending some time getting to know what these are and which resources ...
Supporting careers in defence through specialist education
As a materials engineer by background, I have always been drawn to fields where technical expertise directly shapes real‑world outcomes. Few sectors exemplify this better than defence. Engineering careers in defence sit at the ...





Comments are closed.