Wood in rivers affects invertebrate community traits
11/07/2019

The bed of a river is an important habitat for invertebrates with a diverse range of organisms living within and on the sediment. These invertebrate communities may appear similar at different locations within a river reach, but subtle variations in environmental conditions result in invertebrate species assemblages presenting different characteristics.
For a long time, dead wood has been considered a nuisance in rivers and removed for flood risk, transport, recreation and aesthetic reasons. With changing management practices and new scientific knowledge, wood is beginning to be recognized for its important role driving river processes, both above and below riverbeds, which affect river biodiversity. Yet, how the processes driven by wood affect invertebrate characteristics remains unknown. Functional traits are species characteristics (e.g. body size and form) that reflect adaptation to the surrounding environment, which can provide information on the environmental conditions and pressures to which the species are subjected. To better understand how invertebrates in the bed of rivers respond to wood-induced processes, we explored multiple traits of invertebrates and how they differ at sites where wood is present and absent.
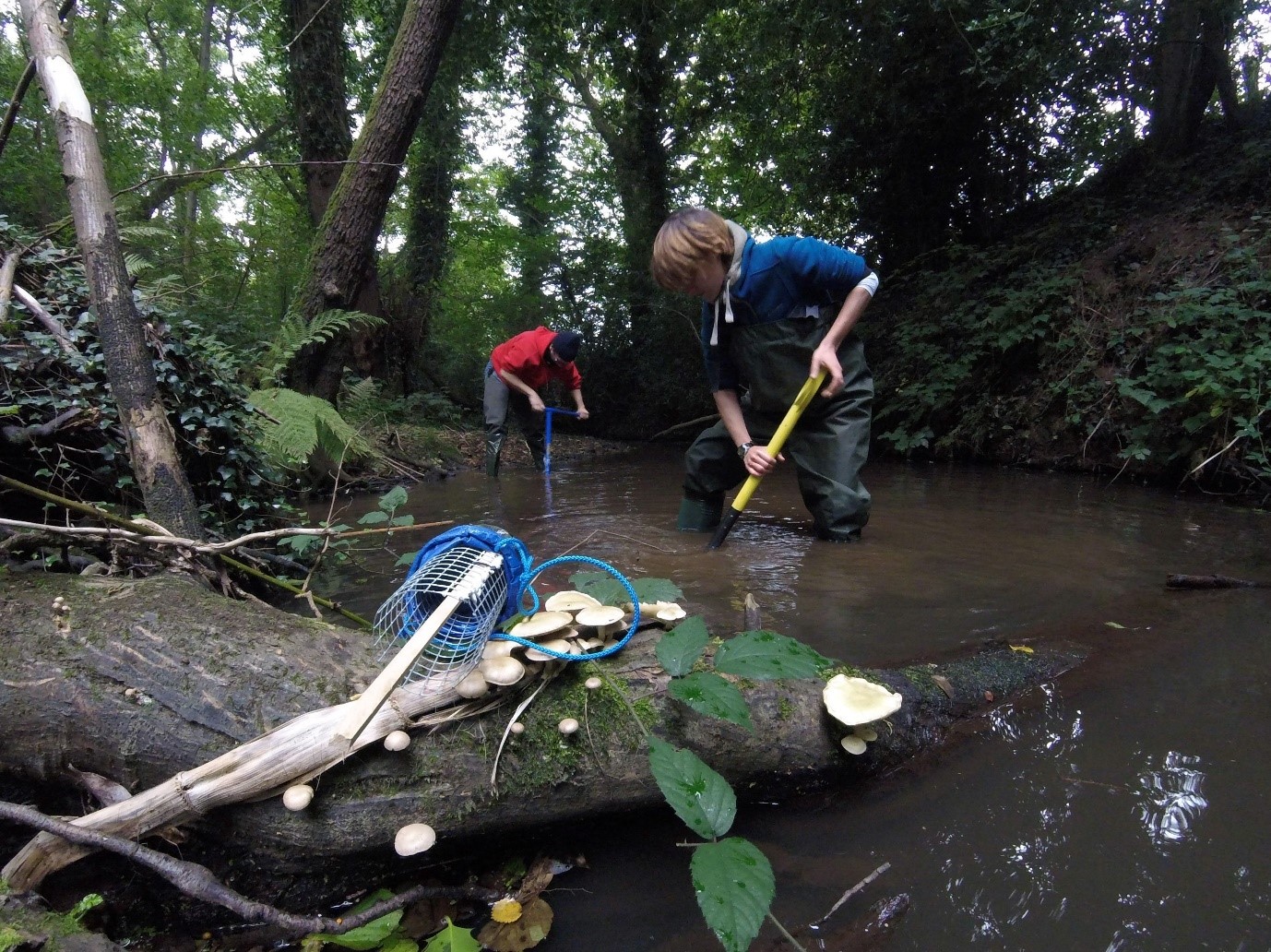
We studied naturally occurring woody debris accumulations in a lowland river in southern England. We sampled invertebrate species living near the surface of the riverbed and deeper in the sediment (see figure). At each sampling site, we also collected environmental information, e.g. sediment type, flow velocity, oxygen and nutrient concentrations, to quantify the variation of traits as a function of environmental variables representing important attributes of wood.
We found that very small invertebrates living more deeply within the sediment had different biological (i.e. aquatic stages, reproduction), physiological (i.e. dispersal, feeding habits) and behavioural (i.e. substrate preferences) traits when found near wood, but the traits of bigger invertebrate living near the riverbed surface did not differ. In the presence of wood, the small invertebrates living below the riverbed were characterized by functional traits that were related to the physical and sedimentological processes occurring around wood (e.g. sediment scour and sorting). The results suggest that wood creates a more dynamic environment with greater variations in local abiotic conditions, resulting in species traits that relate to adaptation to temporal disturbance and spatial refugia. Consequently, the wider ecological effect of wood should be considered when planning river restoration and management solutions.
We found that very small invertebrates living more deeply within the sediment had different biological (i.e. aquatic stages, reproduction), physiological (i.e. dispersal, feeding habits) and behavioural (i.e. substrate preferences) traits when found near wood, but the traits of bigger invertebrate living near the riverbed surface did not differ. In the presence of wood, the small invertebrates living below the riverbed were characterized by functional traits that were related to the physical and sedimentological processes occurring around wood (e.g. sediment scour and sorting). The results suggest that wood creates a more dynamic environment with greater variations in local abiotic conditions, resulting in species traits that relate to adaptation to temporal disturbance and spatial refugia. Consequently, the wider ecological effect of wood should be considered when planning river restoration and management solutions.
For further information read the publication: https://besjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/1365-2435.13381
Categories & Tags:
Leave a comment on this post:
You might also like…
My journey to Cranfield as an FIA Motorsport Engineering Scholar
"You don’t need to fit a stereotype to succeed in engineering or motorsport. You need curiosity. Resilience. And the confidence to take up space." In this blog, Sanya Jain, current MSc student and FIA ...
‘Getting started with Bloomberg’ training – discover the power of Bloomberg terminals
Perhaps you've heard people talking about Bloomberg or heard it mentioned in the news and are wondering what all the fuss is about? Why not come along and find out at our Getting started with ...
Commonwealth Scholarships play a critical role in developing sustainability and leadership in Africa
Q&A with Evah Mosetlhane, Sustainability MSc, Commonwealth Distance Learning Scholar What inspired you to pursue the Sustainability MSc at Cranfield? I was inspired to pursue the Sustainability MSc at Cranfield because of the university’s ...
How do I reference a thesis… in the NLM style?
You may be including theses within your research. When you do so you need to treat them in the same way as content taken from any other source, by providing both a citation and a ...
Introducing… Bloomberg Trade Flows
Are you interested in world trade flows? Would it be useful to know which nations are your country's major trading partners? If so, the Bloomberg terminal has a rather nifty function where you can view ...
Cranfield alumni voyage to the International Space Station
Seeing our alumni reach the International Space Station (ISS) has a ripple effect that extends far beyond the space sector. For school students questioning whether science is “for them”, for undergraduates weighing their next ...