Forecasting – Prediction is very difficult, especially if it’s about the future!
10/07/2017


Niels Bohr, the Nobel laureate in Physics and father of the atomic model, is quoted as saying, “Prediction is very difficult, especially if it’s about the future!” This quote serves as a warning of the importance of testing a forecasting model out-of-sample. It’s often easy to find a model that fits the past data well — perhaps too well! — but quite another matter to find a model that correctly identifies those features of the past data which will be replicated in the future.
So here’s the thing: in the private and public sector, we keep hearing senior executives talking about being more predictive — getting on the front-foot and being less reactive. Almost all of them fail to recognise that unless your business processes, their incoming demand and outgoing outcomes are not “In Control” (meaning in statistical control) then forecasting is worthless — a black art at best! Here’s an example of a process that is not In Control:
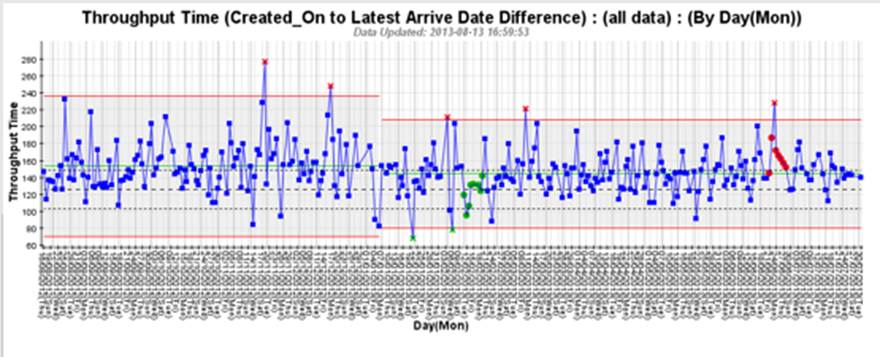
The above processes (there are 2 of them, with a change near the middle of the chart causing a “process break” between the first part of the process and the second part of the process) are not In Control. The chart has a large number of different types of signals, red x indicating unusually long delivery times, green x indicating unusually short delivery times, green • indicating sustained unusually short delivery times and red • indicating sustained unusually long delivery times. Using this data to forecast forwards will produce at best a range of between 80 and 200 (lower and upper red performance corridor guidelines on right part of chart), but because it’s not In Control, there will be occasions when these guidelines will be exceeded. This is because, as Niels Bohr says, the signals indicate that the process contains features that may or may not be replicated in the future.
Looking at a process that is In control:
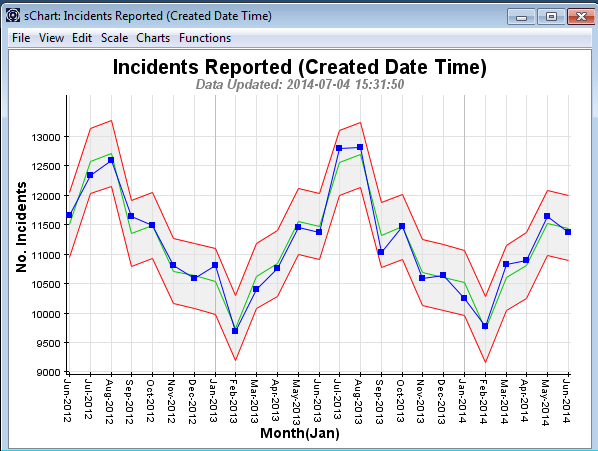
We can see that there are no signals and that the data is following a very strong seasonal pattern. This means the results are likely to be dominated by features of the past that will be replicated in the future. So we can confidently (but not with absolute certainty — there’s always risk, but in this case it is minimised by being In Control) predict what will happen in the future (unless we or the system we are examining make changes):

Thus, we can be pretty sure that the forecast for February 2015 will be around an average (green line bounded by upper and lower red guidelines) of 9,750+500 approx., and for July 2015 will be around an average of 12,500+500 approx.
BUT, if a senior executive says, “I need you to be more precise, I need one number”, you’re up against another well-respected Physicist — Heisenberg and his Uncertainty Principle. The more precise one thing you measure, the fuzzier another becomes. So asking for a forecast which is a single number only (without a range of possible values), means that the probability of it actually occurring approaches zero! Or as Dilbert says, worthless!
Categories & Tags:
Leave a comment on this post:
You might also like…
My journey to Cranfield as an FIA Motorsport Engineering Scholar
"You don’t need to fit a stereotype to succeed in engineering or motorsport. You need curiosity. Resilience. And the confidence to take up space." In this blog, Sanya Jain, current MSc student and FIA ...
‘Getting started with Bloomberg’ training – discover the power of Bloomberg terminals
Perhaps you've heard people talking about Bloomberg or heard it mentioned in the news and are wondering what all the fuss is about? Why not come along and find out at our Getting started with ...
Commonwealth Scholarships play a critical role in developing sustainability and leadership in Africa
Q&A with Evah Mosetlhane, Sustainability MSc, Commonwealth Distance Learning Scholar What inspired you to pursue the Sustainability MSc at Cranfield? I was inspired to pursue the Sustainability MSc at Cranfield because of the university’s ...
How do I reference a thesis… in the NLM style?
You may be including theses within your research. When you do so you need to treat them in the same way as content taken from any other source, by providing both a citation and a ...
Introducing… Bloomberg Trade Flows
Are you interested in world trade flows? Would it be useful to know which nations are your country's major trading partners? If so, the Bloomberg terminal has a rather nifty function where you can view ...
Cranfield alumni voyage to the International Space Station
Seeing our alumni reach the International Space Station (ISS) has a ripple effect that extends far beyond the space sector. For school students questioning whether science is “for them”, for undergraduates weighing their next ...