Team of Teams
13/12/2019

New Rules of Engagement for a Complex World
General Stanley McChrystal
You Tube – https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WH8lMXBVjN8
Summarised by Keith Thompson
Introduction
Business leaders and managers constantly seek to create, and sustain over time, successful and high performing organisations. In his book, McChrystal draws upon his experience of the war against Al Qaeda in Iraq (AQI). As leader of Joint Special Operations Command (JSOC) in this war, the Allied forces were badly losing despite being better funded, trained and equipped. He tells the story of how he learned about and developed the organisation to find and ultimately kill Abu Musab al-Zarqawi the leader of AQI at that time, effectively winning the campaign.
Within this review, some of the key topics covered are:
– Overview of the book
– Key Players
– Insights
– Analysis of Insight
– About the Author
Overview
McCrystal’s second book focuses on his leadership of Joint Special Operations Command (JSOC) in Iraq. The Allied Forces were losing the campaign and McChrystal describes himself realising that the established practices of Command and Control from Scientific Management (Taylorism) were simply not enabling his force to deal with the agile and flat structures of the AQI terrorist network.
He identified that his own organisation was complex and, therefore, would not conform to the rigid established principles developed by Taylor from the 1880’s. The core principles of Taylorism rely on controlling the variables within a production environment, which can be possible within a factory. Within the Iraq environment however, predictability of outcomes is almost impossible with the variation in conditions, complexity of operations and speed of change. The result being the creation of complex (or nonlinear) relationships – meaning a small thing (such as one change of team member, or slight change on location) could have a large impact or none at all.
He recognised the work of IBM in developing the Cynefin Framework (See our previous blogs on the subject) to identify the difference between a complicated domain and a complex domain, and how they should be treated differently.
It was this conflict between complexity and the application of scientific management principles which were holding his force back, while AQI could move and regroup quicker whilst adapting, almost organically, as needed. Essentially, AQI were operating the principles of Mission Command (again see our previous blogs on the subject) better than the Allies and WINNING!
So McCrystal knew things had to transform in order to defeat AQI, but he writes:
‘Little of our transformation was planned. Few of the plans that we did develop unfolded as envisioned. Instead, we evolved in rapid iterations, changing—assessing—changing again’.
Their plan however did have guiding principles:
Have a Common Purpose – Know the mission: to disrupt and disable AQI
Foster Shared Consciousness – His daily 90-minute Operational & Intelligence O&I brief via teleconference with up to 7,000 people worldwide delivering transparency and free flow of information
Empowered Execution – He stopped authorising deadly strikes (he added no value) empowering the task force, as long as the decisions weren’t immoral or illegal
Build Trust – Trust within Teams was great but, between teams needed development. McChrystal created highly skilled people as Liaison Officers working with other teams to improve connections and outcomes
Leader as a Gardener – Changing leadership from commanding to cultivating
Key Players
The book was actually written by a team, but they chose to tell the story from McCrystal’s perspective making the story more personal and compelling. The additional authors were:
Tantum Collins – is a writer and researcher for McChrystal. Having studied for a BA in Global Affairs at Yale he also attended McChrystal’s Course on Leadership
David Silverman – A Former Navy Seal co-founder of the McChrystal Group and founder and CEO of CrossLead
Chris Fussell – is a Managing Partner at McChrystal Group, and the leader of the McChrystal Group Leadership Institute. A Former US Navy SEAL Officer and Aide-de-Camp to McChrystal during his final year leading JSOC. He also is the recognised author of One Mission (another account of McCrystal leading the war on AQI)
Insights
The main Deconstruct for organisations is to create teams within the hierarchy that have:
· A Common Purpose
· An Understanding of the Big Picture
· De-centralised Authority – Empowerment to make Decisions
· Trust (Key elements of military training within Mission Command)
In the book, McCrystal describes how organisations (including the military) have developed since the times of the industrial revolution – effectively around “planning and discipline”. This way of organising is attributed largely to Frederick Winslow Taylor (probably one of the world’s first recognised management consultants). He also recognises Taylor’s methods, although based on Purpose and Intent (as is Mission Command), are mainly focused around reductionism (methods which are highly prevalent in some industries even today).
Over the previous century, where the environment had not changed that quickly on or off the battlefield, these methods may have been appropriate. However, with the advent of the Iraq war, the game had changed fundamentally!
McCrystal still needed to be disciplined, with a plan/outcome, but now needed to be agile and innovative to deal with the Volatile, Uncertain, Complex and Ambiguous (VUCA) conditions within which his highly skilled teams were operating. He recognised that he was fighting against an organisation that had no manual or rules to violate other than to survive and win. This made the enemy incredibly adaptable.
McCrystal likens this to business today with large and highly structured organisations defending against small agile start-ups with flat organisational structures. Which reminds me of the saying “The big don’t eat the small, the fast eat the slow!”
His guiding principles helped shape JSOC to become agile and innovative, delivering significant increases in the number of operations aimed at disrupting and disabling large swathes of AQI.
Analysis of Insights
Team of Teams references many well-known practices within industry, from recognising and improving performance to achieving a mission or a goal. These practices are underpinned by the 4 points of Deconstruct for an organisation: Purpose, Understanding, Authority and Trust. However, there is one key piece of published academic understanding that I believe was achieved unconsciously. Over the last number of years, we have been studying and incorporating the academic work of Luc Hoebeke on Human Based Activity Systems. This work details the importance of relationships and communication for humans delivering outcomes through a shared or distributed process. Hoebeke recognises the importance of the human linkages and the way they impact the commercial system. We believe results of this work are critically overlooked within many Transformation or Improvement projects conducted by most organisations today.
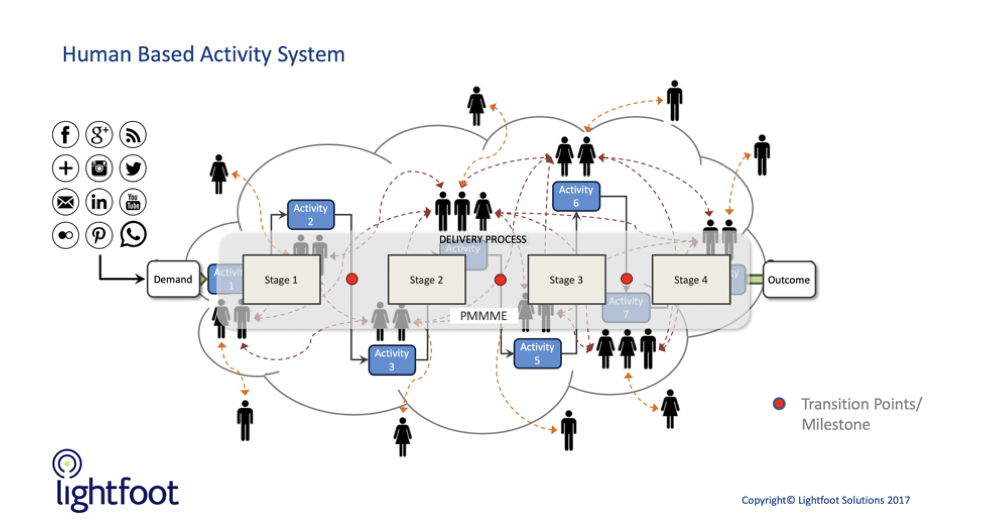
It can be viewed as a facsimile of the working of our own brain. Our brain is made up of a number of parts capable of working independently from each other. However, it is only when these parts behave as one do we really see an effective human being. This development occurs when parts of the brain learn to communicate in order to form habits and behaviours around the way we live our lives. Communication within the brain is commonly referred to as Neural Pathways formed through these habits and behaviours and pathways are strengthened through training and repetition. It is now commonly understood that it is possible to train the brain to reinforce good behaviours or habits and similarly re-train it to remove or reduce the effects of poor behaviours or habits.
Bring this thought back to our process delivery mechanism where the delivery teams are effectively parts of the brain, engineering the ‘Neural Pathways’ of the appropriate strength become a key deliverable for successful outcomes. Similarly, it becomes clear to see why reorganisations within companies result in reduced or poor performance – either permanently or at the very least while the human communication pathways heal / re-establish themselves.
Strong analogies can be drawn from what McCrystal was doing with the human based activities to achieve the mission against AQI. The ‘O&I’ established a mechanism to create these pathways, but it was the introduction of ‘Liaison Officers’ developing the critical communication pathways that gave McCrystal’s organisation the success he achieved in disrupting and disabling AQI
About the Author
As a four star General, General McChrystal has a family history within the American military. His father was a Major General and Grandfather a Colonel. He graduated from West Point in 1976. His Wikipedia page includes much detail about his life, but through his books (My share of the task, Team of Teams and Leaders) the context of Leadership is deeply embedded throughout all his writings.
Categories & Tags:
Leave a comment on this post:
You might also like…
My journey to Cranfield as an FIA Motorsport Engineering Scholar
"You don’t need to fit a stereotype to succeed in engineering or motorsport. You need curiosity. Resilience. And the confidence to take up space." In this blog, Sanya Jain, current MSc student and FIA ...
‘Getting started with Bloomberg’ training – discover the power of Bloomberg terminals
Perhaps you've heard people talking about Bloomberg or heard it mentioned in the news and are wondering what all the fuss is about? Why not come along and find out at our Getting started with ...
Commonwealth Scholarships play a critical role in developing sustainability and leadership in Africa
Q&A with Evah Mosetlhane, Sustainability MSc, Commonwealth Distance Learning Scholar What inspired you to pursue the Sustainability MSc at Cranfield? I was inspired to pursue the Sustainability MSc at Cranfield because of the university’s ...
How do I reference a thesis… in the NLM style?
You may be including theses within your research. When you do so you need to treat them in the same way as content taken from any other source, by providing both a citation and a ...
Introducing… Bloomberg Trade Flows
Are you interested in world trade flows? Would it be useful to know which nations are your country's major trading partners? If so, the Bloomberg terminal has a rather nifty function where you can view ...
Cranfield alumni voyage to the International Space Station
Seeing our alumni reach the International Space Station (ISS) has a ripple effect that extends far beyond the space sector. For school students questioning whether science is “for them”, for undergraduates weighing their next ...