Can we use cleaning products to improve sanitation systems in developing countries?
08/12/2017

Toilets, and how we clean them, very rarely comes up in most people’s conversations. We visit the bathroom, do our business, and with one flush and a hand wash later, all evidence and memory of last night’s dinner is gone, taken far away in a maze of pipes to be dealt with elsewhere. It’s quick, convenient and, most importantly, really sanitary, if done right. When things get a little unpleasant, a squirt of cleaning product is all that’s really required. For millions of people, however, the situation is very different.
Pit latrines – the situation:
In 2013, an estimated 60% of the world’s population did not have access to integrated sewage management systems. In fact, 1.77 billion people worldwide used an ancient form of sanitation, commonplace in Roman times, called a pit latrine. This number is only set to grow as NGOs, including the World Health Organisation (WHO), aim to improve worldwide access to sanitation. Their long-lasting popularity is due to their simplicity, affordability and ease of build, making them a solid choice both for low income countries and in emergency situations, such as natural disasters or refugee camps.
For pit latrines, the waste is not simply carried away. Thankfully, the faecal matter that builds up within the pit latrine is broken down by bacteria both in the faeces and in the surrounding soil. This degradation slows down the filling rate of pit latrines, meaning they have to be emptied less frequently. This is also linked to the inactivation of pathogenic organisms found within pit latrines, so that after approximately a year, the faecal matter at the bottom of a pit latrine contains very few pathogens, making handling the fully degraded faecal matter and its use as a fertiliser far safer.
Cleaning pit latrines
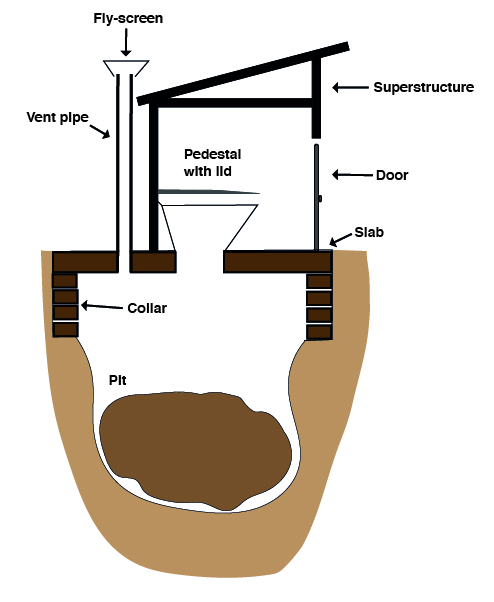
Ventilated Improved Pit Latrine design
Pit latrines, just like any other sanitation system, need to be cleaned and maintained in order to prevent the spread of disease. This is, however, where things get a bit trickier. For toilets, cleaning products are great at what they do; killing microorganisms found on toilet seats and in the toilet bowl, preventing the spread of disease and eliminating odours. Pit latrines would also benefit from having their hard surfaces clean and disease-free. However, the impact of these chemicals once they enter the pit itself is widely unknown.
One concern is that the cleaning products may impact the bacteria responsible for faecal degradation, resulting in a build-up of sludge containing deadly pathogens. Another potential concern is that the cleaning products may contaminate the surrounding environment, including groundwater sources used for drinking water. The by-products formed through the use these chemicals have also been linked to the increased rate of some cancers. Lastly, eliminating the bad smells from a porcelain toilet is one thing, but is a whole different ball game with a pit latrine; the impact cleaning chemicals have on the foul smells rising from the pit is simply not known.
So where do I fit in?
The use of cleaning chemicals for pit latrines has the potential to increase sanitation and reduce disease, making simply doing your business less of a danger to your health. But, before commercial cleaning products can be recommended for use in cleaning pit latrines, it is vital that any potential negative impacts are fully understood and weighed against the positives that come with having a squeaky clean pit latrine. My PhD project will investigate the potential impacts of these cleaning chemicals on processes going on within the pit, how the bacterial community react to the chemicals as well as their effect on pit latrine odours. These dynamics must be fully understood before we can think about using them for the same reasons and in the same way as we do without a second thought in our bathrooms at home.
Categories & Tags:
Leave a comment on this post:
You might also like…
From classroom to cockpit: What’s next after Cranfield
The Air Transport Management MSc isn’t just about learning theory — it’s about preparing for a career in the aviation industry. Adit shares his dream job, insights from classmates, and advice for prospective students. ...
Setting up a shared group folder in a reference manager
Many of our students are now busy working on their group projects. One easy way to share references amongst a group is to set up group folders in a reference manager like Mendeley or Zotero. ...
Company codes – CUSIP, SEDOL, ISIN…. What do they mean and how can you use them in our Library resources?
As you use our many finance resources, you will probably notice unique company identifiers which may be codes or symbols. It is worth spending some time getting to know what these are and which resources ...
Supporting careers in defence through specialist education
As a materials engineer by background, I have always been drawn to fields where technical expertise directly shapes real‑world outcomes. Few sectors exemplify this better than defence. Engineering careers in defence sit at the ...
What being a woman in STEM means to me
STEM is both a way of thinking and a practical toolkit. It sharpens reasoning and equips us to turn ideas into solutions with measurable impact. For me, STEM has never been only about acquiring ...
A woman’s experience in environmental science within defence
When I stepped into the gates of the Defence Academy it was the 30th September 2019. I did not know at the time that this would be the beginning of a long journey as ...