Hard Metrics and Soft Culture
19/09/2017
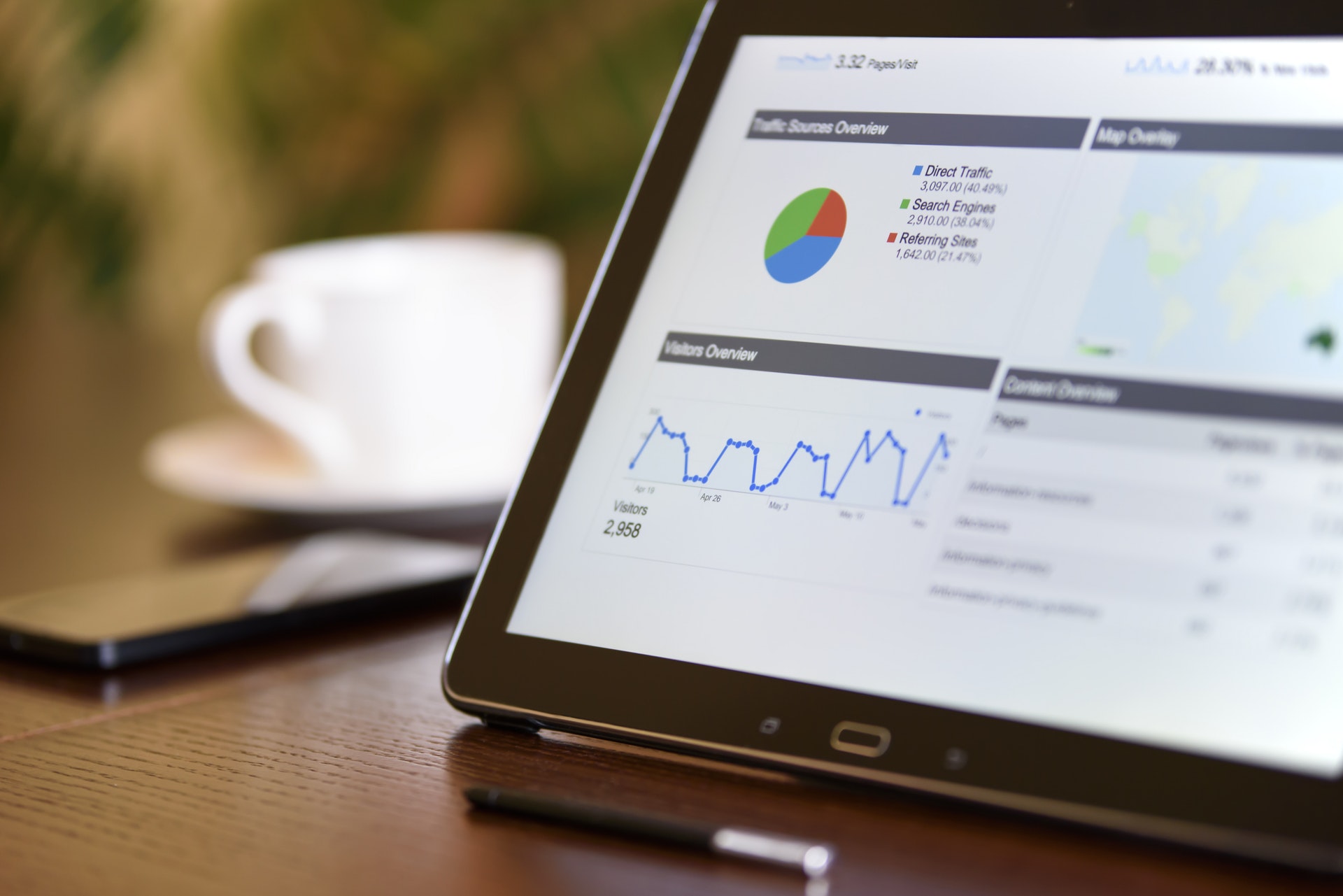

Cranfield is in the process of introducing a new faculty contribution system as part of the performance development review process (PDR). As part of that discussion, yesterday we were talking about the metrics and how they would be used to manage faculty.
Prof Hugh Wilson came up with this phrase, “Hard Metrics and Soft Culture”, which I took to. He was talking about having more facts on which to base the PDR, more real information about what people had done and contributed during the previous year. But he was also talking about how we go about motivating people and doing the development side of the review, rather than just looking at so called “contribution”.
We know from all the research we have done in the Centre for Business Performance that measurement doesn’t improve performance. By itself it does absolutely nothing. It is all about how we use the measures.
Are they sticks to beat people with? In that case they may have a limited positive effect for a short period of time but eventually this approach is doomed to failure. Are they ways of motivating us? This may be laudable, but I would argue that it is a short term solution and, although more acceptable, doomed to failure.
Measurement only makes a difference if it is used to change something that itself will improve performance. That may be the way we work, the improvement in the skills and experience of our staff, the systems we use, the processes we run. It may be that we focus on some things and not on others. But it is the reflection, learning and action that is so important. The rest is just administrative overhead.
Next time I will discuss “Soft Metrics and Hard Culture”.
Mike Bourne
Categories & Tags:
Leave a comment on this post:
You might also like…
Commonwealth Scholarships play a critical role in developing sustainability and leadership in Africa
Q&A with Evah Mosetlhane, Sustainability MSc, Commonwealth Distance Learning Scholar What inspired you to pursue the Sustainability MSc at Cranfield? I was inspired to pursue the Sustainability MSc at Cranfield because of the university’s ...
How do I reference a thesis… in the NLM style?
You may be including theses within your research. When you do so you need to treat them in the same way as content taken from any other source, by providing both a citation and a ...
Introducing… Bloomberg Trade Flows
Are you interested in world trade flows? Would it be useful to know which nations are your country's major trading partners? If so, the Bloomberg terminal has a rather nifty function where you can view ...
Cranfield alumni voyage to the International Space Station
Seeing our alumni reach the International Space Station (ISS) has a ripple effect that extends far beyond the space sector. For school students questioning whether science is “for them”, for undergraduates weighing their next ...
From classroom to cockpit: What’s next after Cranfield
The Air Transport Management MSc isn’t just about learning theory — it’s about preparing for a career in the aviation industry. Adit shares his dream job, insights from classmates, and advice for prospective students. ...
Setting up a shared group folder in a reference manager
Many of our students are now busy working on their group projects. One easy way to share references amongst a group is to set up group folders in a reference manager like Mendeley or Zotero. ...






Mike, Nice observations here! Two points:
1. There are some managers who get measurement mixed up with setting targets/rewards, and in so doing the measures get bastardised to suit certain political aims rather than the good aims of the organisation, and can encourage obtuse behaviour to meet targets rather than understand and improve an organisation’s performance.
2. We’ve found extrinsic (i.e. use of targets) motivation of individuals is short-term and often damaging (per above), and have found that by using a so-called “Outcomes Framework” that links the organisation’s Purpose to Actions at the front-line enabling individuals to see clearly how their contribution impacts Purpose – this generates intrinsic motivation (most of the time) and is much more sustainable.